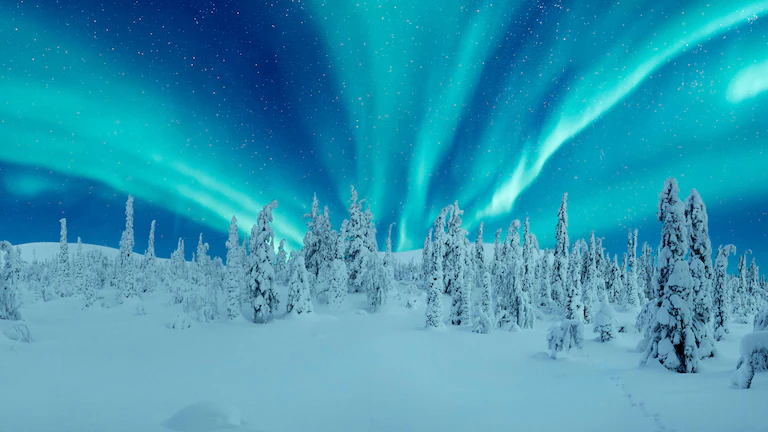


The Boreal Forest
Kaycie, Richard, and AJ
Use this website to guide yourself through a brief description of the boreal forest. This biome covers eight countries where there are freezing temperatures for six to eight months a year.
Characteristics
- Boreal Forest
- General Information
- Cold Sub-Arctic forest region
- Located in Northern Hemisphere
- Location
- High Northern Altitudes
- Usually located between the tundra and the temperate forest, from about 50°N to 70°N
- Located in following countries
- China, Russia,Mongolia, Japan, Norway,Sweden,Iceland,Finland, US, Canada, UK, France
- World's largest biome
- Climate
- Generally Cold
- Capable of promoting vegetation growth, but incapable of supporting prolific tree growth
- Average Temperature
- Mean annual temperatures in the taiga range from a few degrees Celsius above freezing to −10 °C (14 °F) or more
- Average Precipitation Amount
- Approx. 40-50 cm (15-20 inches) a year
- Seasons
- Sharply seasonal patterns mark this climate type. Winters are extremely cold and long, whereas summers are moderately hot and short.

Plants of the Region
Jack Pine Tree
Pine trees are a very common sight throughout boreal forests. Jack pine tree's cones are protected by a natural resin to prevent them from drying out. However, the cones need heat in order to melt the waxy coating and release the seeds.


Strawberry
It may come as a surprise to some people, but strawberries do grow in boreal forests. They grow close to the ground which is their way of surviving the cold conditions in the areas.
Feather Moss
Feather moss is one of the mot widespread moss species in boreal forests. They have adapted to naturally secrete chemical signals that allow them to gain nitrogen in areas that lack it. This nitrogen can be taken from places such as soil or minerals on leaf tissue.


Wild Sarsaparilla
These plants serve as a food source for many animals in boreal forests. Their roots grow very shallow so they they don't yet reach the permafrost layer. However, their roots also spread so that the plant can still get the nutrients that it needs..
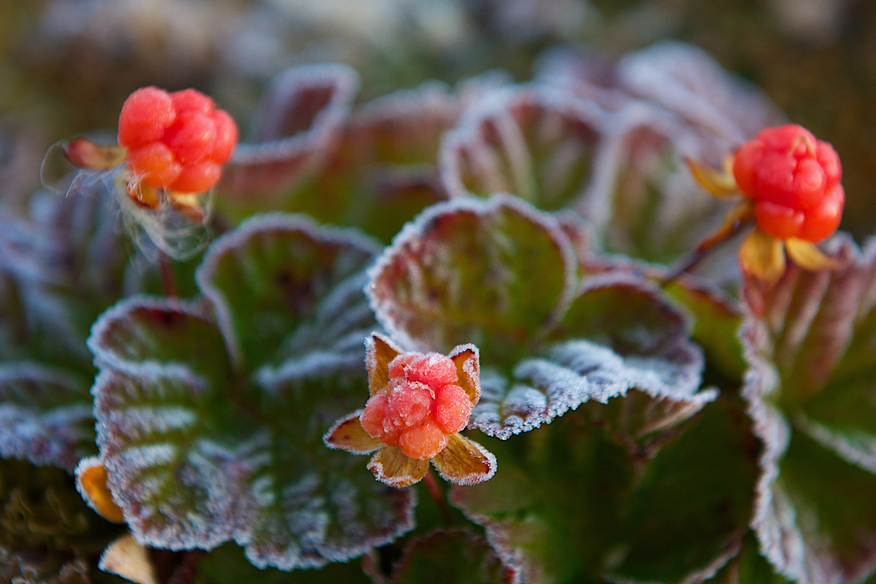
Cloudberry
Otherwise known as the salmonberry, cloudberries are native to northern areas. This has caused this species to be well adapted to the cold weather. They grow on shrubs close to the ground which is how they can manage their cold environment.

Animals of the Region
Beaver
Beavers have lips that can close behind their front teeth, allowing them to eat underwater. They also have big lungs and a slow circulatory system. These things combined help them live under the ice during winter so that they have protection from predators.
Moose
Moose have hooved feet that allow them to stay on top of the snow so that they don't sink into it. This helps them run away from predators faster and get a good grip on slippery surfaces.
Snowshoe Hare
A snowshoe hare's fur changes color with the seasons. this helps it camouflage so that it can stay hidden from predators. Its big feet also help it stay on top of the snow.
Black Bear
Black bears are omnivores, which helps them survive because it makes them less likely to run out of food. Their diet consists of nuts, fruits, twigs, grasses, honey, and fish.
Black Bear
Jack Pine Tree
Food Web
Moose
Cloudberries
Strawberries
Snowshoe Hare
Feather Moss
KEY
Producer
Primary Consumer
Apex Predator
Beaver
Wild Sarsaparilla
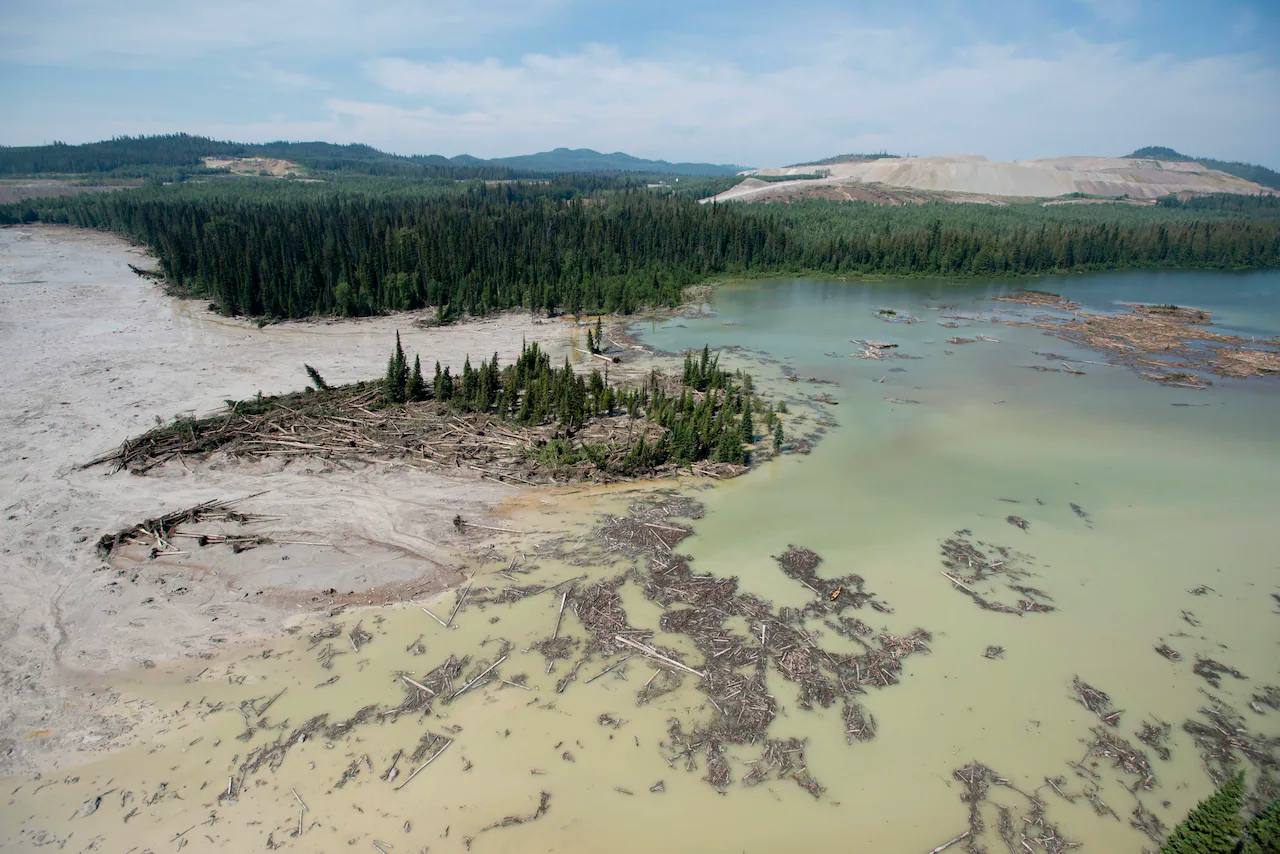

Threats
- Direct threats
- Caused directly by humans
- Logging/Deforestation
- 40% of all logging has occurred in the taiga
- Main source of soft wood in the world
- Approx. 2 million hectares of forest are cleared per year
- Indirect threats
- Caused indirectly by humans/Affected by side effects of listed activities
- Mining
- Deforestation
- Erosion of soil
- Contamination of soil/local streams/wetlands
- Increase in emissions
- Fossil Fuels
- Climate Change
- Hydro-Electric Dams
- Frequent flooding
- 110km of forest flooded
- Disruption of migration patterns
- Contamination of nearby water-sources
- Oil Spills
- Destruction of local ecosystems
- Mining of Tar Sands
- Mixture of sand, clay, water, and bitumen
- Massive reserve of oil
- Creates massive reservoirs of toxic waste known as tailing ponds
- Destroys local ecosystems
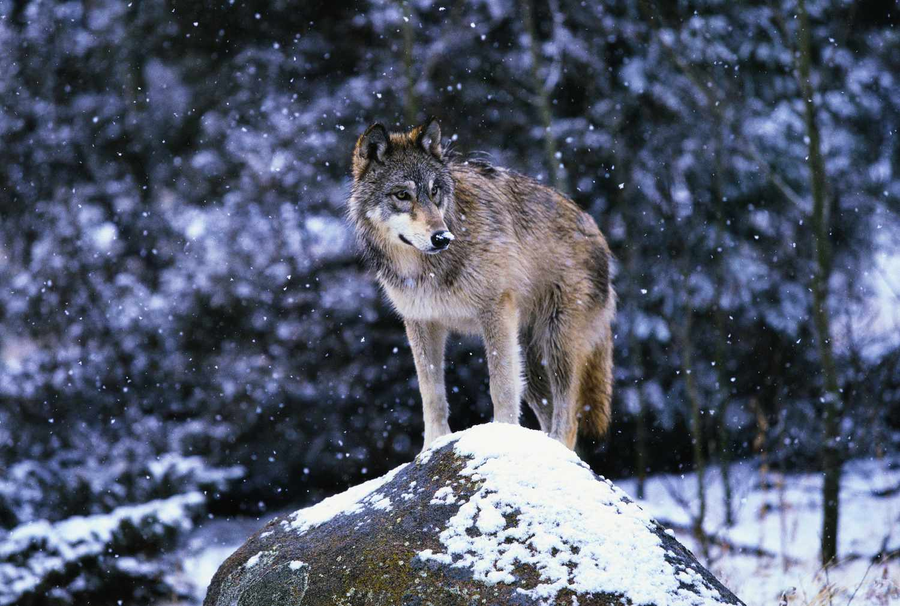

You may be asking....
Why Visit the Boreal Forest?
The boreal forest is home to a huge variety of species. There will be a lot of opportunities to observe them in their natural habitats. Not only are the different organisms fun to take pictures of, but the scenery in boreal forests are always a very lovely sight to see. Lots of opportunity will come to go hiking,, birdwatching, canoeing, and camping during a trip to the boreal forests.
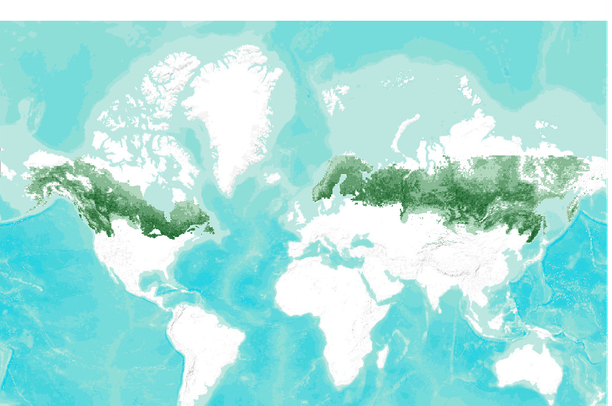
Map
insert here
References
Copyright 2023 This website belongs to the Adventure Science Education Company. This company was founded by AJ Brown, Kaycie Myers, and Richard Sun. All uses of this website without company permission are strictly prohibited. The company is allowed and will charge for abuse of the information given. Charges can start at $5,000 and can reach up to $1,000,000,000 if the website is misused in such ways. Examples of misuse include: Using the information on the website without citing it, using images on the website without citing them, using the company logo without permission, etc. This has been a message brought to you by the Adventure Science Education COmpany. Thank you so much for your support of the website. We hope you enjoyed!